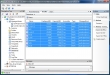
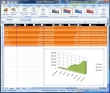
Currently I’m working very hard on my upcoming Dutch VMUG presentation. While I was testing the demo part which is going to be real cool btw, I discovered a real useful feature in the Virtualization EcoShell. The EcoShell Provides pre-defined and customizable reports as well as automated maps without hassle in HTML, XML and CSV formats, including support for Microsoft Visio. But if you want to hassle with XML, what’s the best way? The example screenshots show how to export a selection of data stores to an XML file and then create an Microsoft Excel Map by importing the XML from the file. Excel really does a good job with creating an XML-based representation objects from the EcoShell. The under laying technique is based on the Export-Clixml cmdlet, it creates an XML-based representation of an object or objects and stores it in a file. You can then use the Import-CLIXML cmdlet to re-create the saved object based on the contents of that file. This cmdlet is similar to ConvertTo-XML, except that Export-Clixml stores the resulting XML in a file. ConvertTo-XML returns the XML, so you can continue to process it in Windows PowerShell.
Friday, November 20. 2009
VMware has released vSphere PowerCLI 4.0 U1
VMware vSphere PowerCLI 4.0 Update 1 has been tested against the beta release of vSphere 4.1. To find the related issues, see Known Issues, Compatibility with VMware vSphere 4.1 Beta.
What's New in This Release?
This release of vSphere PowerCLI 4.0 Update 1 introduces the following new capabilities:
•Managing the failover and load-balancing policies of VirtualSwitch and VirtualPortGroup objects with Get-NicTeamingPolicy and Set-NicTeamingPolicy.
•Copying files in and out of guest operating systems with Copy-VMGuestFile.
•Restarting virtual machines with Restart-VM.
•Managing the power state of hosts using Start-VMHost, Restart-VMHost, Suspend-VMHost, and Stop-VMHost.
•Managing guest networks with Get-VMGuestNetworkInterface, Set-VMGuestNetworkInterface, Get-VMGuestRoute, New-VMGuestRoute, Remove-VMGuestRoute, and Set-VMGuestRoute.
•Retrieving and removing USB devices with Get-UsbDevice and Remove-UsbDevice.
•Managing NIC customization settings with Get-OSCustomizationNicMapping, New-OSCustomizationNicMapping, and Set-OSCustomizationNicMapping.
•Handling virtual machine questions with Get-VMQuestion and Set-VMQuestion.
•Working with host storages and iSCSI HBA devices with Get-VMHostHba, Set-VMHostHba, Get-iScsiHbaTarget, New-iScsiHbaTarget, Remove-iScsiHbaTarget, Set-iScsiHbaTarget, and Set-VMHostStorage.
•Moving templates with Move-Template and Move-Inventory.
•Managing the access control system with Get-VIPrivilege, Get-VIRole, New-VIRole, Remove-VIRole, Set-VIRole, Get-VIPermission, New-VIPermission, Remove-VIPermission, and Set-VIPermission.
•Managing DRS recommendations with Get-DrsRecommendation and Apply-DrsRecommendation.
•Upgrading hosts with Install-VMHostPatch.
•Managing virtual appliances with Get-VApp, Export-VApp, Import-VApp, New-VApp, Remove-VApp, Set-VApp, Start-VApp, and Stop-VApp.
•Managing PCI and SCSI passthrough devices with Add-PassthroughDevice, Get-PassthroughDevice, and Remove-PassthroughDevice.
•Running BAT (Windows) and BASH (Linux) scripts with Invoke-VMScript.
•Granting and revoking shell access with New-VMHostAccount and Set-VMHostAccount.
•Uploading firmware packages with Set-VMHostFirmware.
•Creating virtual machines with thin provisioned disks with New-VM.
•Cloning powered-on virtual machines with New-VM.
•Resizing virtual disks and guest partitions with Set-HardDisk.
•Extending, cloning, inflating, and reallocating virtual hard disks with Copy-HardDisk, New-HardDisk, and Set-HardDisk.
•Managing the host time zones with Get-VMHostAvailableTimeZone and Set-VMHost.
•Working with default Datastore Provider and Inventory Provider drives.
•Working with files and directories in datastores by using the Datastore Provider.
For more information on changes made in vSphere PowerCLI 4.0 Update 1, including deprecations and security enhancements, see the vSphere PowerCLI Change Log.
http://downloads.vmware.com/d/details/sdkwin40u1/ZHcqYmQlcHRiZGVqdA
Monday, November 16. 2009
Project Onyx Alpha Release
Carter Shanklin just released the alpha version of project Onyx trough Twitter and YouTube. Onyx generates PowerShell code to help you solve your toughest automation challenges. See the full demonstration with a complete explanation of how to use Onyx at YouTube. Once you have downloaded Project Onyx (http://blogs.vmware.com/files/onyx_1.5.3607.25516.zip) this video shows you how to use it. I already did some tests and it looks awesome.
Onyx is a standalone application that serves as a proxy between the vSphere Client and the vCenter Server. It monitors the network communication between them and translates it into an executable PowerShell code. Later, this code can be modified and saved into a reusable function or script.
1. To connect to a server, click the "Connect" icon.
2. Enter the IP of the vCenter Server on which you want to work and click Connect.
3. Connect with any of the following clients:
For vSphere Client, in the "IP Address" field enter the following address:
http:// [IP of the machine where Onyx is running] : [listening port]
For vSphere PowerCLI, run the following command:
Connect-VIServer [IP of the machine where Onyx is running] -Protocol http
-Port [listening port] -User [username] -Pass [password]
4. To start the generation of PowerCLI.NET scripts, click the "Start" icon.
5. To save the generated script, click the "Save output to file" icon.
Note: To run the generated script, use VMware vSphere PowerCLI.
Free download at: http://www.vmware.com/go/powercli
Monday, November 2. 2009
Just upgraded the Viru-Al.net VESI PowerPack
 One of the coolest PowerShell scripters in the universe has just released version 14 of his VESI PowerPack. I’m talking about a fellow vExpert Alan Renouf, he created a real cool VESI PowerPack which can be downloaded freely at his website. This PowerPack is able to check a lot of things in your VMware environment like showing a list of VMs with inconsistent folder names, ESX NTP settings, Primary HA Nodes and Last VMs created....
One of the coolest PowerShell scripters in the universe has just released version 14 of his VESI PowerPack. I’m talking about a fellow vExpert Alan Renouf, he created a real cool VESI PowerPack which can be downloaded freely at his website. This PowerPack is able to check a lot of things in your VMware environment like showing a list of VMs with inconsistent folder names, ESX NTP settings, Primary HA Nodes and Last VMs created....