vSphere 5.0 can be confgured to enable VMware ESXi host swapping to a solid-state disk (SSD). In the low host memory–available states (high memory usage), where guest ballooning, transparent page sharing (TPS) and memory compression have not been sufcient to reclaim the needed host memory, hypervisor swapping is used as the last resort to reclaim memory from the virtual machines. vSphere employs three methods to address limitations of hypervisor swapping to improve hypervisor swapping performance.
Sunday, January 29. 2012
Video - Configure ESXi host swapping to a solid-state disk
vSphere 5.0 can be confgured to enable VMware ESXi host swapping to a solid-state disk (SSD). In the low host memory–available states (high memory usage), where guest ballooning, transparent page sharing (TPS) and memory compression have not been sufcient to reclaim the needed host memory, hypervisor swapping is used as the last resort to reclaim memory from the virtual machines. vSphere employs three methods to address limitations of hypervisor swapping to improve hypervisor swapping performance.
Thursday, January 26. 2012
Video - Installing vCenter Server 5.0 - Quick Start
VMware vCenter Server allows you to centrally manage hosts from either a physical or virtual Windows machine, and enables the use of advanced features such as vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), vSphere High Availability (HA), vSphere vMotion, vSphere Storage vMotion, and vSphere Auto Deploy. You can install vCenter Server in a Microsoft Windows virtual machine that runs on an ESXi host. Deploying the vCenter Server system in the virtual machine has the following advantages:
- You can provide high availability for the vCenter Server system by using vSphere HA.
- You can migrate the VM containing vCenter from one host to another.
- You can create snapshots of the vCenter Server virtual machine.
- Rather than dedicating a separate server to the vCenter Server system, you can place it in a virtual machine running on the same host where your other virtual machines run.
This video will show you how to install VMware vCenter Server 5.0 in a virtual machine 13 simple steps.
Step 1 > In the software installer directory, double-click the autorun.exe file to start the installer.
Step 2 > Select vCenter Server.
Step 3 > Follow the prompts in the installation wizard to choose the installer language, agree to the end user patent and license agreements, enter your user name, organization name, and license key.If you omit the license key, vCenter Server will be in evaluation mode, which allows you to use the full feature set for a 60-day evaluation period.
Step 4 > Choose the type of database that you want to use.
Step 5 > Set the login information for vCenter Server.
Step 6 > Either accept the default destination folders or click Change to select another location.
Step 7 > Select Create a standalone VMware vCenter Server instance or Join Group.Join a Linked Mode group to enable the vSphere Client to view, search, and manage data across multiple vCenter Server systems. S
Step 8 > If you join a group, enter the fully qualified domain name and LDAP port number of any remote vCenter Server system.
Step 9 > Enter the port numbers that you want to use or accept the default port numbers.
Step 10 > Select the size of your vCenter Server inventory to allocate memory for several Java services that are used by vCenter Server. This setting determines the maximum JVM heap settings for VMware VirtualCenter Management Webservices (Tomcat), Inventory Service, and Profile-Driven Storage Service. You can adjust this setting after installation if the number of hosts in your environment changes. See the recommendations in the vCenter Server Hardware Requirements topic in System Requirements.
Step 11 > (Optional) In the Ready to Install the Program window, select Select to bump up the ephemeral port value. This option increases the number of available ephemeral ports. If your vCenter Server manages hosts on which you will power on more than 2000 virtual machines simultaneously, this option prevents the pool of available ephemeral ports from being exhausted.
Step 12 > Click Install. Installation might take several minutes. Multiple progress bars appear during the installation of the selected components.
Step 13 > Click Finish.
Monday, January 23. 2012
What happens to resource pools when vCenter goes down?
Andy Cary who works as a Senior Technical Trainer at VMware responded immediately with: I created a RP on my vCenter and turned off expandable reservations for memory. Placed VM1 under said resource pool and failed to power up because the VM need to reserve memory for the overhead of running the VM (had no reservations set on the RP). So next I directly connected to the host and powered on the VM with no problem at all. However when you go back to the vCenter it displays:
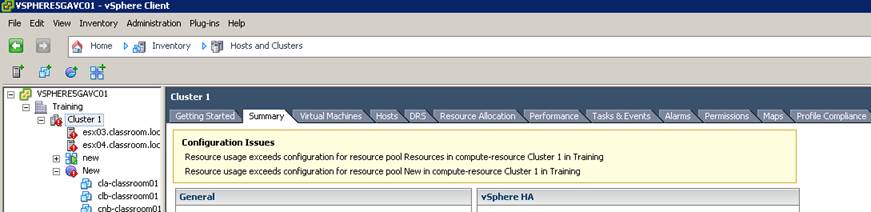
The Cluster with the RP is now invalid because it can see the VM has powered on. So the configuration about DRS RP is saved on the vCenter but it doesn’t stop you going directly to the host an powering on the VM. Now in vSphere 5.0 if you directly connect to a host and try and create a local resource pool it will throw up an error saying this isn’t allowed because it can see you are managed by vCenter, this is the case even if the Host isn’t a member of DRS cluster. So the creation and management of RP is done via vCenter, if vCenter goes down the rules cannot be applied so you could get admin powering on VMs by directly connecting to the hosts. So in summary all we have done is said “You can only create, modify resource pools via vCenter and not by directly connecting to the host”
Saturday, January 21. 2012
White Paper - Mobility and Disaster Recovery Solution for Virtualized Tier-1 Enterprise Applications
 To meet ever growing IT infrastructure needs and to ensure business continuity in case of a site-level disaster, it is critical to have live mobility and fully automated, efficient disaster recovery (DR) processes for virtualized enterprise applications across data centers. Failure to have a robust and efficient mobility and fully automated disaster recovery solution can result in millions of dollars of lost revenue and employee productivity.
To meet ever growing IT infrastructure needs and to ensure business continuity in case of a site-level disaster, it is critical to have live mobility and fully automated, efficient disaster recovery (DR) processes for virtualized enterprise applications across data centers. Failure to have a robust and efficient mobility and fully automated disaster recovery solution can result in millions of dollars of lost revenue and employee productivity.http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Data_Center/DCI/4.0/EMC/mobdisasterrecapps.html
Friday, January 20. 2012
Video - Install vSphere Syslog Collector and configure ESXi logging
Thursday, January 12. 2012
Forbes Guthrie has released the vSphere 5 vReference Card
 The card is available under a Creative Commons license, so feel free to copy and distribute this in paper or electronic format. Just check back frequently to www.vReference.com for updates, or subscribe to the RSS feed to be the first to know.
The card is available under a Creative Commons license, so feel free to copy and distribute this in paper or electronic format. Just check back frequently to www.vReference.com for updates, or subscribe to the RSS feed to be the first to know. Forbes Guthrie: At long last, the vSphere 5.0 vReference Card is ready. Go and grab it over here. This time I’ve split it up into both an A4 version and a separate Letter size one. This should hopefully make the printing experience more consistent regardless of which side of the pond you try.New with this release is a full page version. This is the same information as the card, but I’ve increased the font to a less eye-ball screamingly small font. This should make it make much more conducive to reading as a study guide, or if you want to bone-up on a particular area.
Forbes Guthrie: At long last, the vSphere 5.0 vReference Card is ready. Go and grab it over here. This time I’ve split it up into both an A4 version and a separate Letter size one. This should hopefully make the printing experience more consistent regardless of which side of the pond you try.New with this release is a full page version. This is the same information as the card, but I’ve increased the font to a less eye-ball screamingly small font. This should make it make much more conducive to reading as a study guide, or if you want to bone-up on a particular area.Tuesday, January 3. 2012
VMware KB: Upgrading to vCenter Server 5.0 best practices
VMware supports in-place upgrades on 64-bit systems from vCenter Server 4.x to vCenter Server 5.0. You can upgrade VirtualCenter 2.5 Update 6 or later and vCenter Server 4.0.x to vCenter Server 5.0 by installing vCenter Server 5.0 on a new machine and migrating the existing database.
This upgrade method makes it possible to upgrade from a 32-bit system to a 64-bit system. Alternatively, if the VirtualCenter or vCenter Server database is on a remote machine, you can upgrade the database. vCenter Server 5.0 can manage ESX 3.5.x/ESXi 3.5.x hosts in the same cluster with ESX 4.x/ESXi 4.x hosts.
You cannot upgrade a vCenter Server 4.x instance that is running on Windows XP Professional x64 Edition to vCenter Server 5.0, because vCenter Server 5.0 does not support Windows XP Professional x64. This article provides information about upgrading to vCenter Server 5.0.


