This white paper investigates how VMware Virtual SAN™ performs and scales for well understood synthetic workloads, Virtual SAN caching tier designs, and Virtual SAN configuration parameters. The goal is to provide guidelines on how to get the best performance for applications deployed on a Virtual SAN cluster.
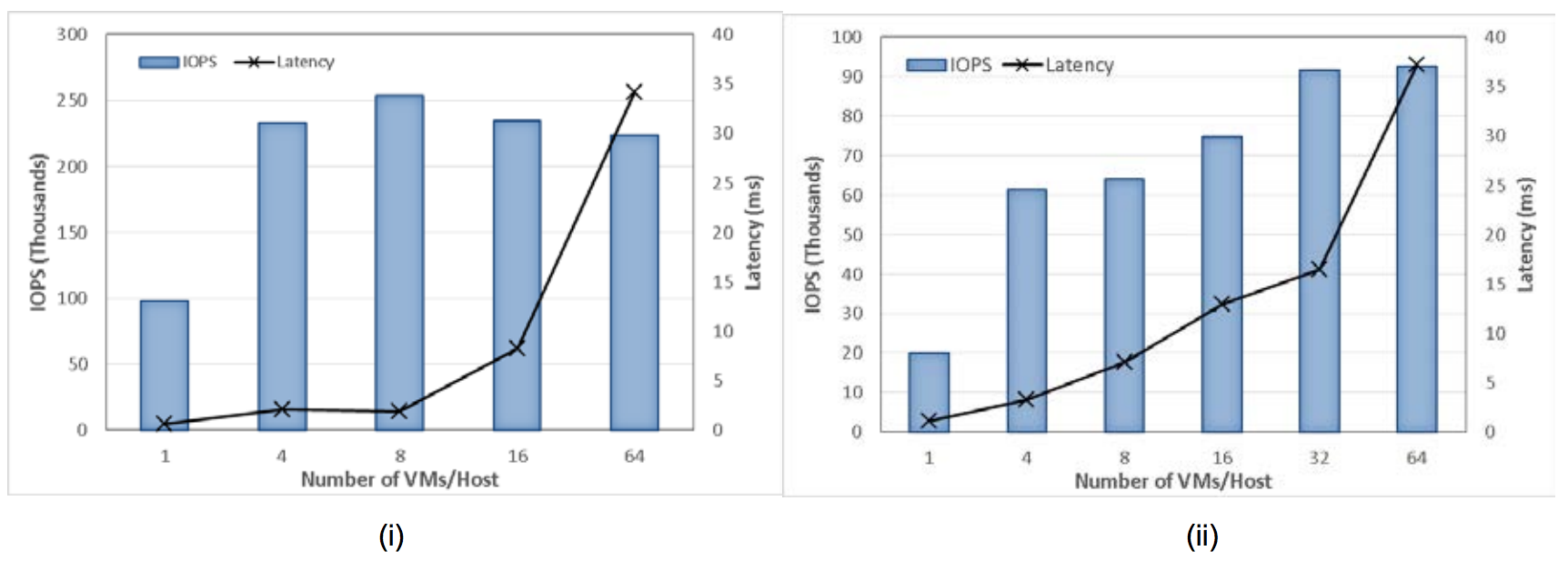

Tests show that the Hybrid Virtual SAN Cluster performs extremely well when the working set is fully cached for random access workloads, and also for all sequential access workloads. The All-Flash Virtual SAN cluster, which performs well for random access workloads with large working sets, may be deployed in cases where the working set is too large to fit in a cache.
All workloads scale linearly in both types of Virtual SAN clusters—as more hosts are added and more disk groups per host, Virtual SAN sees a corresponding increase in its ability to handle larger workloads. Virtual SAN offers an excellent way to scale up the cluster as performance requirements
All workloads scale linearly in both types of Virtual SAN clusters—as more hosts are added and more disk groups per host, Virtual SAN sees a corresponding increase in its ability to handle larger workloads. Virtual SAN offers an excellent way to scale up the cluster as performance requirements
increase.


